Maserati Khamsin Tyres
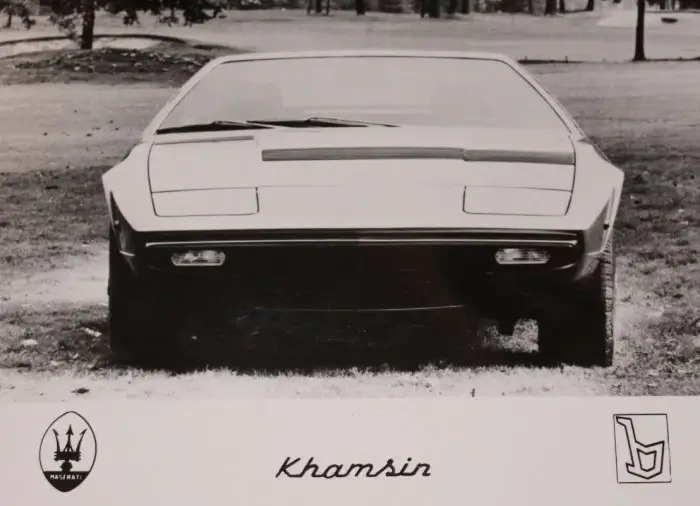

Maserati Khamsin on PIRELLI CINTURATO CN12 Tyres
Maserati Khamsin 1974–1982
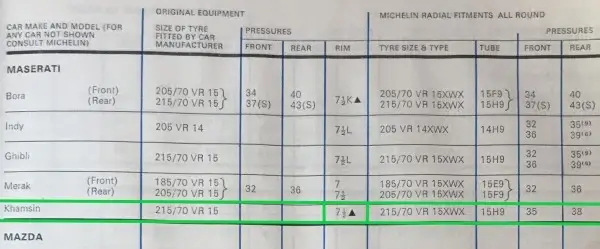
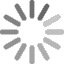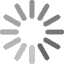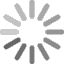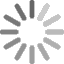
- The Maserati Khamsin fitted 215/70 R15 tyres.
- The 1974 Maserati Khamsin owners manual below lists 215/70VR15 Michelin XWX on 7.5” wheels with 2.4Bar (35psi) front and 2.6Bar (38psi) rear, and shows Michelin XWX tyres in the picture.
- The period Michelin fitment guides for the Maserati Khamsin recommends 215/70VR15 Michelin XWX with 35psi front and 38psi in the rear.
- Period Press photographs of the Khamsin show 215/70 R 15 96W PIRELLI CINTURATO CN12 tyres fitted, for which Pirelli also recommend 35psi and 38psi.
- Longstone recommends either the Michelin XWX or the PIRELLI CINTURATO ™ CN12 for the Maserati Khamsin.

Maserati Full Line Brochure 1979 Khamsin with XWX Tyres
- Our period Innertube Guide suggests that the Khamsin had tubeless wheels from the outset. Innertubes are not required for these wheels to function providing your wheel rims are still airtight.
- The correct tube for 215/70 R15 tyres is the Michelin 15/17H innertube.
- Our period Fitment Guides suggest that the Khamsin fitted tubeless wheels, innertubes are not required on these wheels. We do not have a record of the wheel type for the first 2 years of production, so early models may have tube-type wheels fitted.
- Find a Maserati Khamsin Road Test and Specifications sheet below.

Maserati Khamsin Specifications and Road Test
Maserati Khamsin History
The Maserati Khamsin is a grand tourer manufactured by the Italian automaker Maserati from 1974 to 1982. The Khamsin debuted as a concept car on the Bertone exhibit at the Turin Auto Show in November 1972. It was Bertone's debut effort for Maserati, designed by Marcello Gandini.
In contrast to its predecessor, the Khamsin had a transparent rear portion that held the tail lights as well as a crisp, angular style. The production model debuted at the Paris Motor Show in March 1973. The vehicle's regular manufacturing began barely a year later, in 1974.
The Khamsin was created under Citroen ownership for a customer that desired a front-engined grand tourer in the style of the earlier Ghibli, a more traditional offering than the mid-engined Bora. The body of the Khamsin is distinctively wedge-shaped, with a fastback roofline and kammback rear end. The tail has a full-width glass back panel with inset "floating" tail lights.
When combined with the large, practically all-glass back hatch, this provided superior rear vision in contrast to most cars, particularly equivalent sports cars. The C-pillar has cosmetic triangle vented panels inlaid, with the right panel concealing the gasoline filling cap. The bonnet, which is punctured by asymmetrical vents, is another unique characteristic. Gandini's signature may be found on design elements such as the wedge body, glazed tail panel, and position of the filling cap. All of them were present in his previous Lamborghini Espada.
Despite being marketed as a 2+2, the leather-trimmed back seats, tucked between the two fuel tanks, were deemed to be too cramped for comfort. The instruments on the instrument panel comprised a speedometer, tachometer, water temperature, oil temperature, oil pressure, voltmeter, and a clock.
The Khamsin was built entirely of steel, with a Silentbloc-bushing insulated tubular subframe supporting the rear suspension and differential. The suspension was double wishbones all around, a significant advance over the Ghibli's leaf-sprung solid axle, with coaxial springs and shock absorbers (single up front, double down back), and anti-roll bars. Maserati's 4.9 L, 16-valve V8 engine from the Ghibli SS was retained and produced 240 kW (330 PS; 320 horsepower) at 5,500 rpm.
Maserati Khamsin Tyre Fitment and Innertube Guides

Michelin Fitment Guide Key